
Copper Tube Busbars: The Silent Revolution in Power Transmission Infrastructure
Subtitle: How Hollow Tubular Conductors Are Redefining Efficiency in Energy Systems While Traditional Solutions Grapple with Space and Performance Limitations.
Technological Transformation: From Solid Conductors to Three-Dimensional Power Transmission
The global energy infrastructure upgrade is driving unprecedented demand for copper tube busbars. While representing only 2%–3% of total copper tube demand, these products are experiencing growth rates exceeding 200% annually in applications such as ultra-high-voltage substations, data centers, and new energy power plants. The core advantage lies in their hollow tubular structure, which expands the conductor surface area by 3-5 times, ensures uniform current distribution along the tube wall, reduces the skin effect coefficient below 0.8, and decreases AC resistance by 40% compared to rectangular busbars of equivalent cross-sectional area.
This structural innovation addresses critical challenges in high-current transmission. In 750kV gas-insulated switchgear (GIS), a Φ100×5mm copper tube busbar can carry 4000A current with a density of just 2.68A/mm², while equivalent rectangular busbars require multiple stacked layers, increasing losses by over 30%. More significantly, the mechanical strength of copper tube busbars reaches four times that of rectangular busbars, enabling suspended spans of 9 meters and supported spans extending to 13 meters under 50kA short-circuit current impact, substantially reducing substation steel structure requirements.
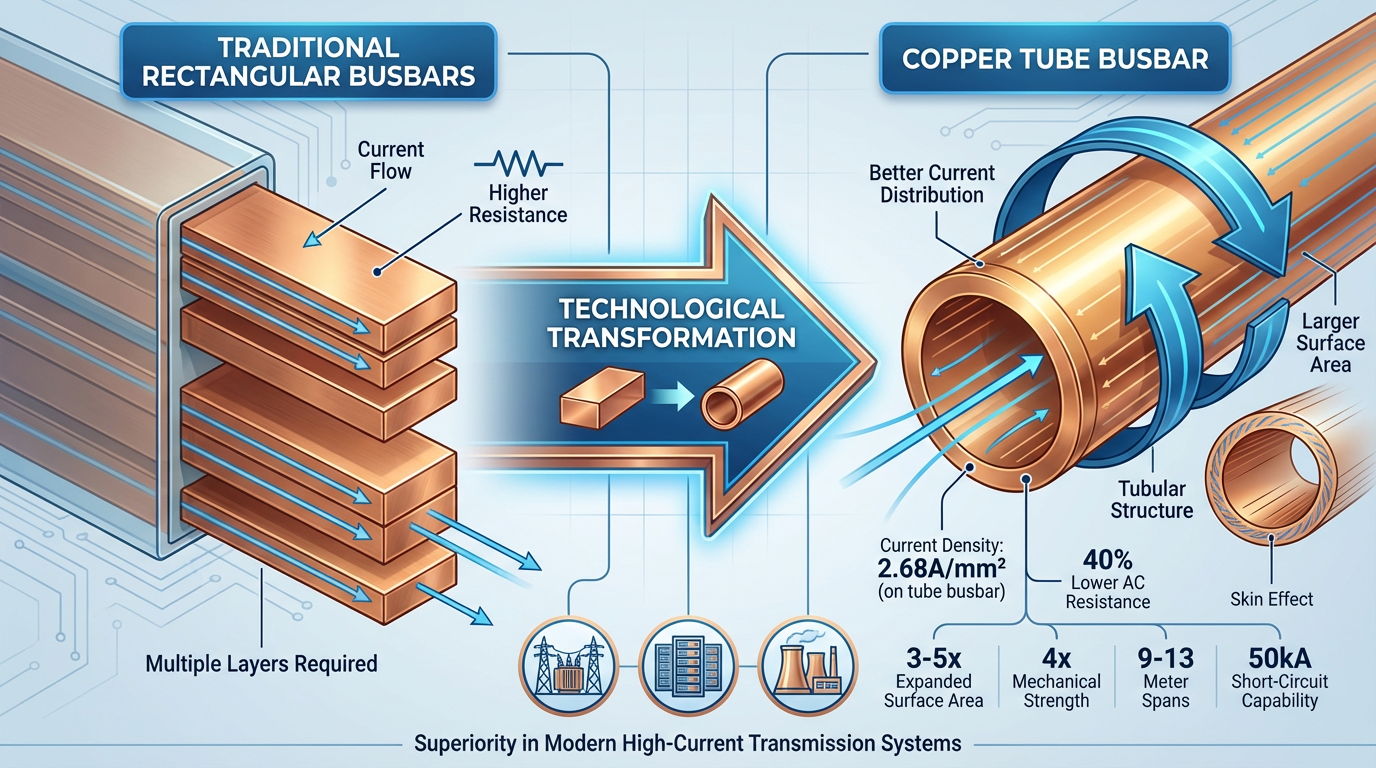
(This image was generated by AI.)
Table: Performance Comparison of Copper Tube Busbars vs. Traditional Rectangular Busbars (2025)
|
Performance Indicator |
Traditional Rectangular Busbars |
Copper Tube Busbars |
Improvement |
|
AC Resistance |
Baseline |
40% reduction |
Efficiency leap |
|
Heat Dissipation |
Dependent on external heat sinks |
Natural convection in inner cavity + optimized outer wall |
60% improvement |
|
Space Occupancy |
Multiple stacked layers occupy large space |
Single-tube replacement, compact structure |
25% space saving |
|
Short-Circuit Withstand |
Prone to deformation requiring reinforcement |
Mechanical strength increased by 4 times |
Safety breakthrough |
|
Installation Cost |
Multiple connectors, complex construction |
Modular splicing, labor time halved |
Economic optimization |
Material Innovation: Advanced Alloys and Sustainable Manufacturing
The performance superiority of copper tube busbars stems from material science breakthroughs. New copper-silver and copper-chromium alloys maintain conductivity while increasing strength by 30%, allowing for thinner walls and material savings of up to 25% without compromising performance. These advanced materials enable operation in temperatures ranging from -196°C to 250°C, making them suitable for extreme environments from cryogenic applications to high-temperature industrial settings.
Sustainable manufacturing processes are reshaping production economics. Modern facilities employ closed-loop water cooling systems that reduce water consumption from 28 cubic meters per ton to 16 cubic meters per ton, a 43% reduction. The integration of 5G and industrial Internet technologies allows real-time energy optimization, cutting comprehensive energy consumption per unit product by 30%. These advancements not only lower production costs but also help products qualify for exemptions under mechanisms like the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
Application Spectrum: From Traditional Power to New Energy Frontiers
The value proposition of copper tube busbars is being redefined across multiple sectors. In ultra-high-voltage direct current transmission, ±800kV converter stations using fully insulated copper tube busbars report system losses reduced by 18%, with annual operational cost savings reaching $4 million. This advantage becomes particularly pronounced in long-distance transmission, where projects exceeding 100 kilometers benefit from lifecycle cost reductions of 25% or more.
The renewable energy sector represents a particularly promising frontier. In wind farm applications, copper tube busbars demonstrate reliable operation at -40°C, with UV-resistant coatings extending outdoor service life to 30 years—double the 15-year cycle of traditional cables. In photovoltaic power stations, modular designs accelerate installation by 50%, proving especially valuable for rapidly deployable distributed energy projects. Rail transit represents another growth vector, with systems like the Shanghai Metro Line 14 achieving traction converter efficiency of 98.5% and train energy consumption reduction of 7% after adopting Φ120×8mm copper tube busbars.
Regional Landscape: Global Variations in Adoption and Innovation
The global copper tube busbar market exhibits distinct regional characteristics. Europe maintains leadership in high-end applications, with German manufacturers holding 60% of the high-purity tube market. North America focuses on aerospace and defense applications, where specialized alloys meet extreme performance requirements. Meanwhile, Chinese companies have made significant advances in niche segments such as marine-grade B10 nickel-copper tubes, capturing 25% of the global market share.
This geographic distribution reflects differing competitive advantages. European dominance in premium segments stems from long-standing expertise in precision manufacturing, while North American strengths align with its advanced aerospace industry. China's rise benefits from integrated industrial clusters that combine upstream smelting, midstream processing, and downstream applications, reducing R&D cycles by 30% and costs by 20%.
Future Directions: Smart Systems and Next-Generation Materials
The future evolution of copper tube busbars points toward greater intelligence and functionality. The integration of fiber optic sensors enables real-time monitoring of temperature, stress, and partial discharge, with some industrial applications achieving 92% accuracy in equipment fault prediction and reducing unplanned downtime by 65%. This transformation elevates copper tube busbars from passive conductive elements to active energy management nodes.
Next-generation materials promise further breakthroughs. Copper-graphene composites demonstrate thermal conductivity five times that of pure copper at one-fourth the weight, while superconducting variants operating at -196°C liquid nitrogen temperatures offer zero-resistance power transmission. Although not yet commercially viable at scale, these advanced materials point toward a future where copper tube busbars could see weight reductions of 60% while simultaneously improving performance.
System integration represents another key direction. Combined cooling-conduction integrated busbars that merge heat dissipation with power transmission functions can reduce connector counts by 30% while increasing energy density. This approach exemplifies the industry's shift from component manufacturing to integrated solution provision.
Product Category
Content
- Technological Transformation: From Solid Conductors to Three-Dimensional Power Transmission
- Material Innovation: Advanced Alloys and Sustainable Manufacturing
- Application Spectrum: From Traditional Power to New Energy Frontiers
- Regional Landscape: Global Variations in Adoption and Innovation
- Future Directions: Smart Systems and Next-Generation Materials
Related news
-

What is a thick-walled copper tube? Thick-walled copper tube, also known as seamless thick-walled copper tube, is a high-performance metal tube made o...
See Details -

Overview and Importance of Copper Capillary Tube In modern industrial equipment and precision control systems, miniaturization and high precision have...
See Details -

What is a copper tube? Analysis of material composition and basic characteristics Definition of copper tube Copper tube is a tubular object made of co...
See Details -

Understanding Copper Square Tubes: Composition, Grades, and Typical Applications Copper square tubes are specialized extrusions that combine the super...
See Details

 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文