
Battery Precision Cooling Tubes: Can a "Small Component" Truly Reshape EV Performance?
Subtitle: While traditional metal tubes struggle in price wars, a niche product with ±0.03mm wall thickness tolerance commands prices of ¥250,000–350,000 per ton—how does this segment, representing less than 5% of total copper tube capacity, achieve over 30% gross margin?
Demand Breakout: EV Performance Race Drives High-End Market Growth
In 2025, global sales of new energy vehicles exceeded 40 million units, fueling explosive demand for precision cooling tubes used in battery thermal management systems. Although these products account for only 6%–8% of the total copper tube market, they contribute over 20% of industry profits. Unlike standard construction-grade copper tubes (priced at ¥60,000–80,000/ton), battery cooling tubes sell for ¥180,000–350,000/ton, with gross margins reaching 25%–35%.
This surge is driven by the EV performance race. As battery energy density increases, thermal management requirements become more stringent. For example, a 10% rise in energy density raises heat dissipation needs by 15%. High-power fast charging (e.g., 800V platforms) demands extreme precision: temperature variations between cells must be kept within ±2°C to prevent a 30% reduction in battery lifespan. Thus, precision cooling tubes have become critical components for safety and performance.
Table: Battery Cooling Tubes vs. Traditional Copper Tubes (2025)
|
Indicator |
Traditional Tubes |
Battery Cooling Tubes |
Gap |
|
Price Range |
¥60,000–80,000/ton |
¥180,000–350,000/ton |
3–5x |
|
Gross Margin |
3%–5% |
25%–35% |
6–8x |
|
Growth Rate |
2%–3% annually |
28%–32% annually |
10x |
|
Tech Barrier |
Standardized production |
±0.03mm wall tolerance |
High entry threshold |
(This image was generated by AI.)
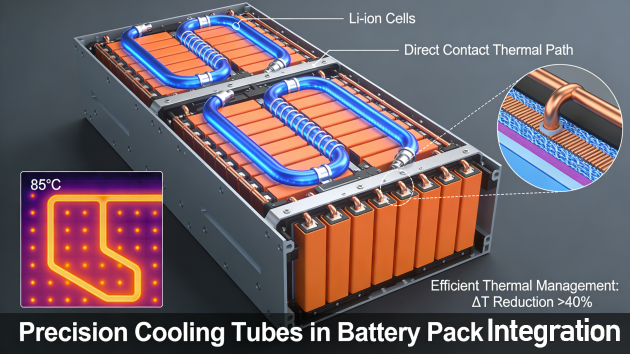
Technical Barriers: The Precision Battle Behind ±0.03mm Tolerance
The core competitiveness lies in ultra-high-precision manufacturing. EV battery packs have limited space, requiring cooling tubes to maximize surface area within tight constraints. Wall thickness tolerance must be controlled within ±0.03mm, and bending radius errors must not exceed 0.1mm—10 times stricter than traditional tubes.
Material innovations are breakthroughs. Tesla’s multi-channel microporous cooling tubes feature 240 micro-holes (0.5mm diameter) on the inner wall, increasing coolant contact area by 300% and improving heat dissipation efficiency by 40%. Such designs rely on laser drilling + electrochemical polishing, with equipment investments exceeding ¥20 million, creating high entry barriers.
Process control directly impacts product lifespan. Leading companies use online eddy current detection systems to perform 1,280 point inspections per meter of tube, reducing defect rates to below 0.3‰. Traditional manufacturers relying on random sampling typically see defect rates of 3%–5%.
Competitive Landscape: Europe Leads in High-End, China Breaks into Niche Markets
The global battery cooling tube market shows a clear technological gradient:
- Europe: Dominates high-end sectors (e.g., medical, semiconductor), with German giants like Wieland holding 60% of the high-purity tube market;
- North America: Focuses on aerospace and defense, with companies like Materion supplying tubes for rocket engine cooling;
- China: Excels in niche areas like marine-grade B10 nickel-copper tubes, capturing 25% of the global market share.
Chinese companies’ rise benefits from industrial chain collaboration. For example, Yingtan City’s "copper-based new materials cluster" integrates upstream smelting, midstream processing, and downstream applications, reducing R&D cycles by 30% and costs by 20%.
Future Trends: Material Revolution and System Integration
Next-generation batteries are driving cooling tube innovations. Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL)'s Qilin battery uses large-area cell cooling technology, requiring 100% contact between tubes and cells. This drives demand for embossed copper tubes with micro-dots on the surface, which improve thermal conductivity by 25% but cost three times more than standard tubes.
System integration is another key direction. BYD’s cooling-conduction integrated tubes combine heat dissipation and high-voltage current transmission, reducing connectors by 30% and increasing battery pack volume utilization to 72%. Such products require multi-physics design capabilities beyond traditional tube manufacturers.
Alternative materials pose challenges. Aluminum cooling plates cost 40% less than copper tubes and have captured 35% of the low-end EV market. Carbon nanotube composites offer five times the thermal conductivity of copper at one-fourth the weight, though not yet commercially viable.
Small Components, Big Impact
Battery precision cooling tubes, though a niche segment, are becoming decisive factors in EV performance. As global EV adoption advances, this market will grow at a 25%+ annual rate. Companies that lead in material innovation, precision manufacturing, and system integration will capture the high-value segment of this transformative industry.
Product Category
Content
Related news
-

What is a thick-walled copper tube? Thick-walled copper tube, also known as seamless thick-walled copper tube, is a high-performance metal tube made o...
See Details -

Overview and Importance of Copper Capillary Tube In modern industrial equipment and precision control systems, miniaturization and high precision have...
See Details -

What is a copper tube? Analysis of material composition and basic characteristics Definition of copper tube Copper tube is a tubular object made of co...
See Details -

Understanding Copper Square Tubes: Composition, Grades, and Typical Applications Copper square tubes are specialized extrusions that combine the super...
See Details

 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文