
The Silent Disruption: When Copper Tubes Become Data Pipes - A Tale of Two Industries
Subtitle:Beyond fluid and heat conduction, a new breed of smart copper tubes is emerging as critical data infrastructure, fundamentally challenging the identity and business models of traditional manufacturers.
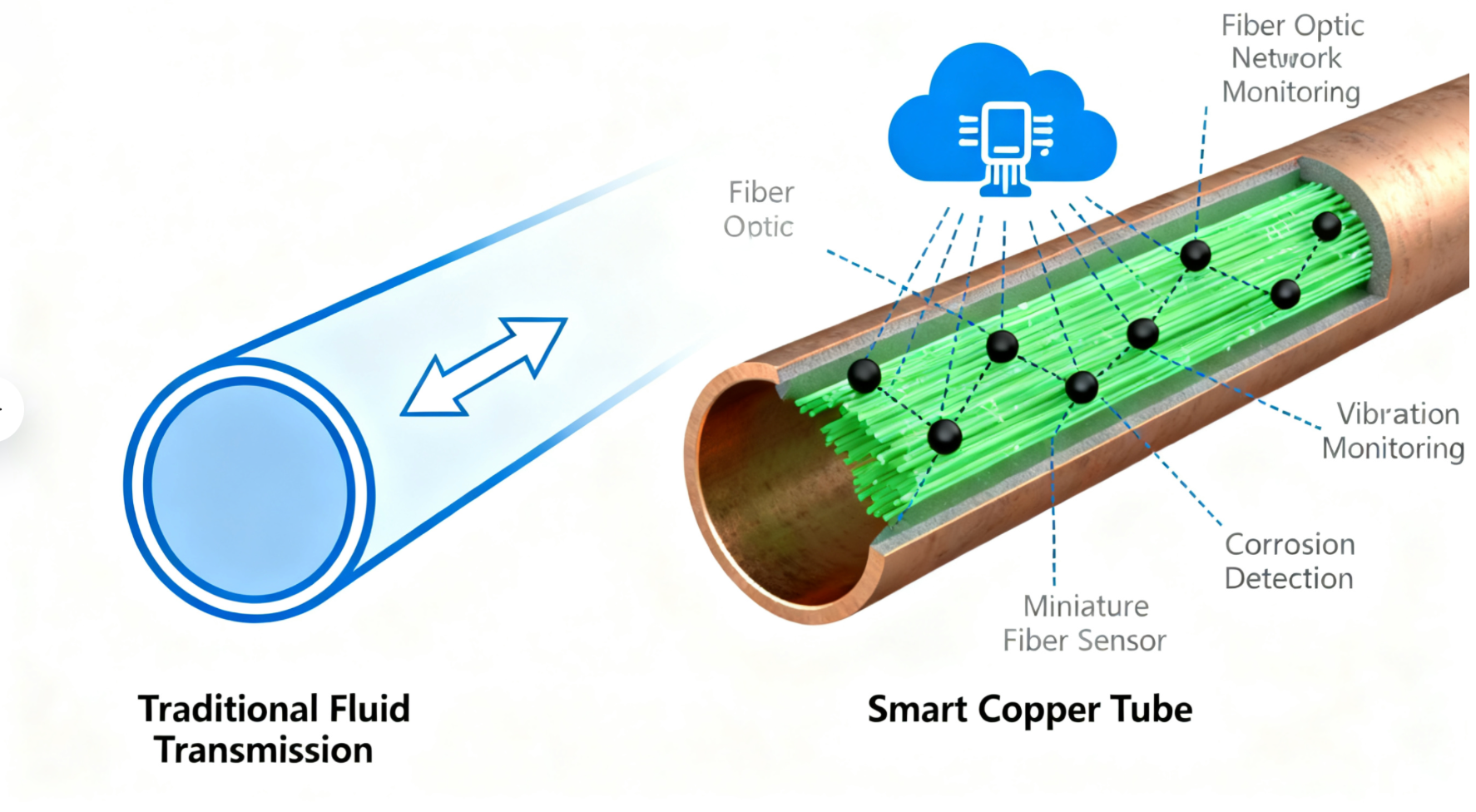
(Caption: From passive pipe to active sensor: The fundamental evolution of the copper tube's role, from a mere conductor of substances to a generator and transmitter of operational intelligence.)
The copper tube, one of the most established industrial components, is experiencing an identity crisis. For centuries, its value was defined by a simple, physical metric: how efficiently it moved water, refrigerant, or gas. Its condition was a mystery, only revealed through failure. Today, a seismic shift is underway, bifurcating the industry into two irreconcilable paths. On one side lies the traditional commodity tube, a passive component competing on cost per meter. On the other, the rise of the smart, data-generating tube, an active sentinel within mechanical systems, whose value is measured not in kilograms, but in the critical operational intelligence it provides. This divergence isn't just about adding features; it's about redefining the product's very soul and business model.
The Incumbent: The "Dumb" Pipe - A Commodity on Borrowed Time
The traditional copper tube business is a masterpiece of optimized mass production, but its paradigm is increasingly fragile.
- The Value Proposition: Cost and Conductivity.The equation is simple: deliver a reliable, standardized product at the lowest possible price. Competition revolves around sourcing cheaper cathode copper, improving drawing efficiency, and minimizing logistics costs.
- The Business Model: Value is exchanged once, at the point of sale. The manufacturer's relationship with the tube typically ends at the factory gate.
- The Critical Limitation - The "Black Box": Once installed, the tube becomes a passive, unmonitored component. Engineers have no insight into internal corrosion rates, wall thinning, micro-cracks, or flow efficiency degradation. Maintenance is either reactive (fixing leaks) or blindly preventive (scheduled replacements), leading to costly downtime or unnecessary waste.
"A leak in a critical cooling system in a data center can cause millions in damage per hour. Yet, with traditional tubes, we're essentially flying blind until it's too late," laments a facility manager for a hyperscaler, highlighting the core vulnerability.
The Disruptor: The "Smart" Tube - From Conduit to Cognitive Component
The new paradigm transforms the tube from a silent piece of metal into the nervous system of the infrastructure it serves.
- The Technology Core: This involves integrating fiber optic sensors (Distributed Acoustic Sensing/Acoustic Sensing) or micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) directly into the tube wall or during installation. These sensors can continuously monitor a range of parameters in real-time:
-
- Structural Health: Strain, vibration, and acoustic emissions indicative of fatigue or impingement.
- Wall Thickness: Direct measurement of corrosion rates.
- Temperature & Flow: Precise thermal and hydraulic performance data.
- The Data Value: This constant stream of data enables a shift from preventive to predictive maintenance. The system can alert operators to a potential failure months in advance, allowing for planned, non-emergency intervention. It also enables operational optimization, revealing inefficiencies in heat exchange or fluid dynamics.
"The tube is no longer just part of the cooling system; it's the diagnostic tool for the entire system," explains a project lead at a company developing these solutions.
The Great Schism: A Comparative Analysis
The difference between these two product philosophies is profound, impacting every aspect of the business.
|
Dimension |
Traditional "Dumb" Pipe |
Smart, Data-Generating Pipe |
|
Primary Value |
Lowest Cost per Meter |
Operational Uptime & Risk Mitigation |
|
Key Metric |
$ / kg |
Data Availability, Predictive Accuracy** |
|
Manufacturer's Role |
Component Supplier |
Long-term Service & Solutions Partner |
|
Revenue Model |
One-time Transaction |
Initial Sale + Recurring Data Service Fees |
|
Customer Relationship |
Transactional, Price-Sensitive |
Strategic, Partnership-Based |
|
R&D Focus |
Process Efficiency, Cost Reduction |
Material Science, Sensor Integration, Data Analytics |
|
Competitive Moats |
Scale, Logistics, Raw Material Access |
IP on Sensor Fusion, Analytics Algorithms, Service Reliability |
|
Keyword |
Commodity |
Mission-Critical Insurance |
The Business Model Upheaval: Selling Pipes vs. Selling "Uptime"
This technological shift forces a complete reinvention of the business model. Smart tube manufacturers are no longer just selling a product; they are selling an outcome: system reliability.
- From Capex to Opex: Customers may pay a significant premium for the smart tube itself (Capital Expenditure) and then a recurring subscription fee for the data analytics platform and monitoring service (Operational Expenditure).
- Value-Based Pricing: The price is justified by the immense cost of failure it prevents. For a nuclear power plant, a semiconductor fab, or a hyperscale data center, the value of avoiding unplanned downtime dwarfs the additional cost of the smart tubing system.
- New Ecosystem Players: This disruption opens the door for new entrants: specialized sensor companies, data analytics firms, and even traditional tube manufacturers who can pivot to master both materials science and data science.
The Roadblocks: Challenges on the Path to Pervasive Intelligence
The vision is compelling, but the path is fraught with challenges that the traditional model does not face.
- Cost and Complexity: Integrating sensors and ensuring their longevity in harsh environments (high pressure, temperature, chemical exposure) is complex and expensive.
- Data Standardization and Security: How is data formatted, transmitted, and stored? In critical infrastructure, the data pipeline must be as secure as the physical one, raising significant cybersecurity concerns.
- Cultural Resistance and Skills Gap: Traditional engineering and procurement teams are accustomed to evaluating unit cost. Adopting this new model requires a shift to valuing total cost of ownership (TCO) and risk mitigation. It also requires new skills in data interpretation.
The Inevitable, Asymmetric Future
The copper tube industry is not facing a simple upgrade, but an asymmetric disruption. The traditional commodity market will not disappear; it will continue to thrive in cost-sensitive, low-risk applications. However, the high-value, high-stakes segment of the market will be irrevocably captured by smart tube providers.
The manufacturers that will dominate the future are not necessarily those with the biggest furnaces today, but those who can best fuse metallurgical expertise with digital intelligence. The great silent disruption of the copper tube is a powerful metaphor for the wider world of industrial components: in the age of AI and IoT, even the most fundamental physical objects are being reimagined as sources of insight, creating new winners and relegating those who only see metal to the sidelines. The question is no longer just what the tube is made of, but what it knows.
Product Category
Content
- The Incumbent: The "Dumb" Pipe - A Commodity on Borrowed Time
- The Disruptor: The "Smart" Tube - From Conduit to Cognitive Component
- The Great Schism: A Comparative Analysis
- The Business Model Upheaval: Selling Pipes vs. Selling "Uptime"
- The Roadblocks: Challenges on the Path to Pervasive Intelligence
- The Inevitable, Asymmetric Future
Related news
-

What is a thick-walled copper tube? Thick-walled copper tube, also known as seamless thick-walled copper tube, is a high-performance metal tube made o...
See Details -

Overview and Importance of Copper Capillary Tube In modern industrial equipment and precision control systems, miniaturization and high precision have...
See Details -

What is a copper tube? Analysis of material composition and basic characteristics Definition of copper tube Copper tube is a tubular object made of co...
See Details -

Understanding Copper Square Tubes: Composition, Grades, and Typical Applications Copper square tubes are specialized extrusions that combine the super...
See Details

 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文