
Copper vs. Aluminum: Why Copper Evaporator Tubes Are the Best Choice for Cooling Systems
When it comes to designing and manufacturing cooling systems—whether for air conditioning, refrigeration, or HVAC systems—selecting the right material for key components such as evaporator tubes is crucial to the system’s performance, energy efficiency, and longevity. Two materials that often come into play in this decision are copper and aluminum. Both metals are commonly used in the production of evaporator tubes, but copper has emerged as the preferred choice for a variety of reasons.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
One of the most important factors in selecting materials for cooling systems is thermal conductivity. The goal of evaporator tubes is to efficiently transfer heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air, ensuring that the cooling system operates at maximum efficiency.
-
Copper has an outstanding thermal conductivity of approximately 398 W/mK, making it one of the most effective materials for heat transfer. This high thermal conductivity means that copper evaporator tubes can rapidly absorb and release heat, significantly improving the cooling performance of the system.
-
Aluminum, while also a good conductor of heat, has a thermal conductivity of around 235 W/mK—about 40% less than copper. This lower thermal conductivity means aluminum evaporator tubes take longer to transfer heat, potentially reducing the overall cooling efficiency.
As cooling systems demand high-efficiency performance, copper evaporator tubes outperform their aluminum counterparts in providing faster and more effective heat exchange.
| Characteristic | Copper Evaporator Tubes | Aluminum Evaporator Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent thermal conductivity (398 W/mK) for efficient heat transfer | Lower thermal conductivity (235 W/mK), less efficient heat transfer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Strong corrosion resistance, ideal for humid environments | Prone to oxidation and corrosion, especially in moist conditions |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, can withstand high pressure and mechanical stress | Weaker, more prone to dents, bending, and damage under stress |
| Maintenance & Repair | Easy to solder and repair, low maintenance cost | Harder to repair, complex welding and higher repair costs |
| Fouling Resistance | Naturally resistant to microbial growth, less prone to fouling | Prone to dirt and debris buildup, can harbor bacteria and algae |
| Cost-Effectiveness (Long Term) | Higher initial cost but saves on long-term maintenance and energy costs | Lower initial cost but may lead to higher operational costs due to lower efficiency |
| Environmental Impact | Highly recyclable with lower environmental footprint | Recyclable, but the recycling process consumes more energy |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan, fewer replacements needed | Shorter lifespan, more frequent replacements required |
| Adaptability to High Pressure | Better suited for high-pressure environments, withstands greater pressure | Not suitable for high-pressure environments, more prone to deformation |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy efficiency, reduces operational costs | Lower energy efficiency, may lead to higher energy consumption |
Enhanced Durability and Longevity
Copper has been known for its durability and resistance to corrosion for centuries. When it comes to refrigeration and cooling systems, this durability is a critical factor in ensuring that the system functions optimally over the long term.
-
Copper is highly resistant to corrosion, particularly in environments where moisture and varying temperatures create a risk for degradation. This corrosion resistance means that copper evaporator tubes are more likely to retain their structural integrity and efficiency over many years of use.
-
Aluminum, on the other hand, is more susceptible to oxidation and corrosion, especially in environments where it’s exposed to moisture or high humidity. Over time, aluminum evaporator tubes may degrade, reducing their performance and requiring more frequent maintenance or replacement.
For industrial and commercial applications, where reliability and longevity are crucial, copper’s resistance to corrosion and its ability to maintain its structural integrity make it the superior choice for evaporator tubes.
Better Mechanical Strength
In addition to corrosion resistance, copper also boasts greater mechanical strength compared to aluminum. This strength ensures that copper evaporator tubes can withstand higher pressures, impacts, and mechanical stress without warping or breaking.
-
Copper is a more robust material that can handle the high-pressure environments often found in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Its ability to endure mechanical stress without damage makes it particularly well-suited for systems operating in demanding conditions.
-
Aluminum is lighter and more flexible than copper, but this also means that it’s less resistant to damage from external forces. In high-pressure environments, aluminum evaporator tubes are more prone to denting, cracking, or bending, which can compromise their performance and longevity.
For high-pressure systems or those that experience vibration or physical stress, copper’s superior mechanical strength makes it a more reliable choice.
Easier to Maintain and Repair
Over time, cooling systems may experience wear and tear that requires maintenance or repair. Copper evaporator tubes are often preferred in these situations because they are easier to maintain and repair compared to their aluminum counterparts.
-
Copper is easier to solder and weld, allowing for quick repairs and modifications if necessary. Additionally, copper components can be easily replaced without compromising the performance of the system.
-
Aluminum, while lightweight, can be more challenging to repair. Welding aluminum requires special techniques and equipment, and repairs are often more complex, leading to higher maintenance costs.
The ease of maintenance and repair of copper evaporator tubes makes them an attractive option for systems where downtime and repair costs need to be minimized.
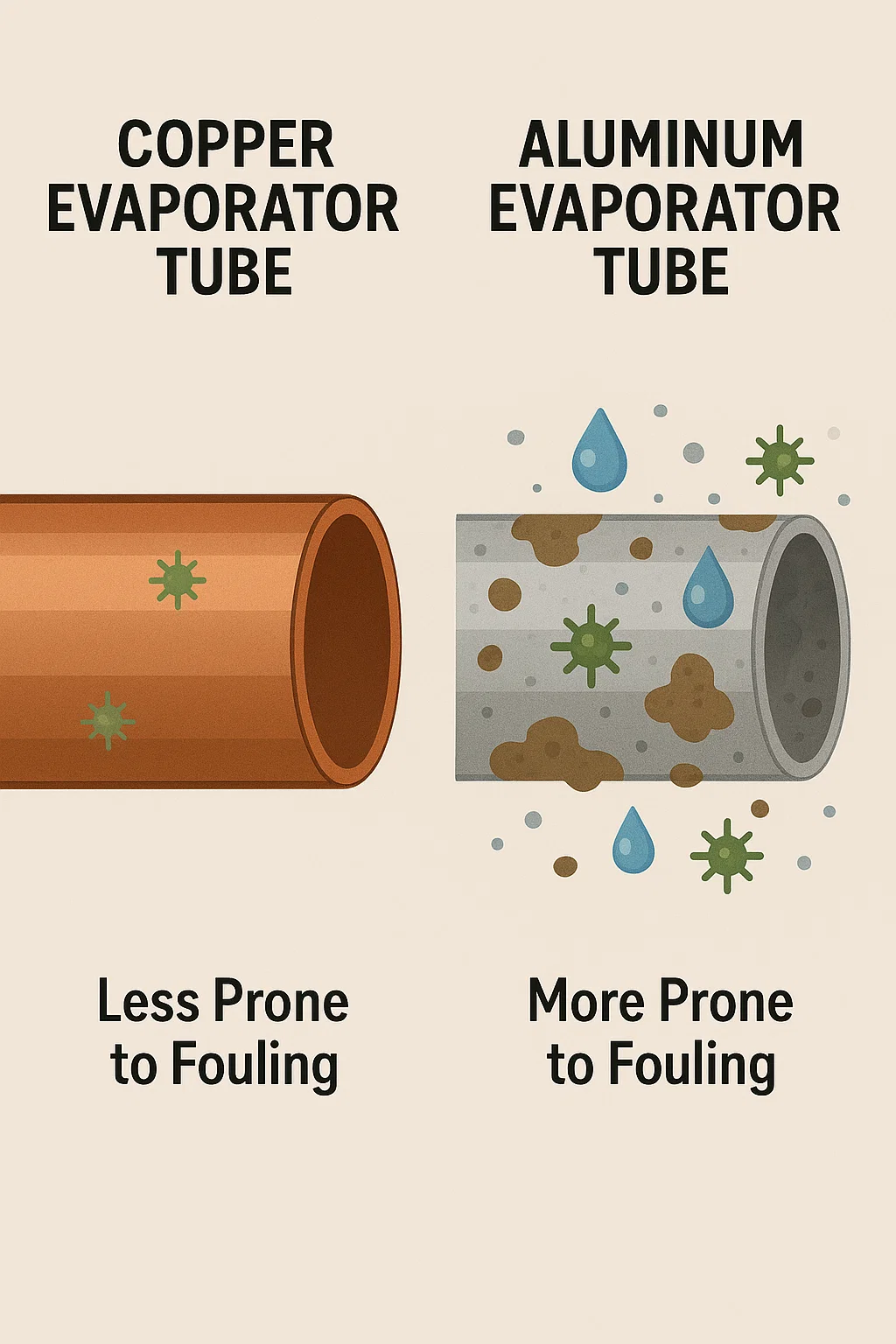
Resistance to Fouling
Fouling is a common issue in cooling systems, where dirt, moisture, and other contaminants accumulate on heat exchanger surfaces, reducing the system’s performance. Copper evaporator tubes are less prone to fouling than aluminum, as their surface properties inhibit the buildup of contaminants.
-
Copper has natural antimicrobial properties that help prevent the growth of bacteria, fungi, and algae on its surface. This resistance to fouling keeps copper evaporator tubes cleaner and more efficient over time, reducing the frequency of cleaning and maintenance.
-
Aluminum, while it does resist corrosion, is more prone to fouling. The surface of aluminum tubes can attract dirt and debris more easily, and the presence of moisture can create a breeding ground for bacteria and algae. This leads to reduced efficiency and the need for more frequent cleaning and servicing.
By reducing the buildup of contaminants, copper helps maintain optimal performance and energy efficiency in the long term.
Higher Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run
While copper evaporator tubes may come with a higher upfront cost compared to aluminum, they offer greater cost-effectiveness over time. The initial investment in copper pays off through lower maintenance costs, fewer repairs, and greater energy efficiency.
-
Energy Efficiency: Copper’s superior thermal conductivity ensures better heat transfer, meaning that cooling systems with copper evaporator tubes are more energy-efficient. This can lead to lower operational costs and reduced energy consumption over time.
-
Longevity: Copper’s resistance to corrosion, fouling, and mechanical wear means that systems with copper evaporator tubes have a longer lifespan. Fewer replacements and repairs mean that businesses or homeowners save on replacement costs and avoid the downtime associated with system failures.
In comparison, although aluminum may have a lower initial cost, the higher maintenance costs and lower efficiency could make it more expensive in the long run.
Environmental Impact
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in all industries, the environmental impact of materials used in cooling systems is a growing consideration.
-
Copper is a highly recyclable material and has a relatively low environmental footprint compared to other metals. It can be reused without significant loss of quality, making it a more environmentally friendly choice.
-
Aluminum is also recyclable but often requires more energy in the recycling process. Additionally, its lower durability means it may need to be replaced more frequently, contributing to more waste over time.
Given copper’s sustainability and recyclability, it is a better choice for companies and individuals looking to minimize their environmental impact.
Product Category
Related news
-

What is a thick-walled copper tube? Thick-walled copper tube, also known as seamless thick-walled copper tube, is a high-performance metal tube made o...
See Details -

Overview and Importance of Copper Capillary Tube In modern industrial equipment and precision control systems, miniaturization and high precision have...
See Details -

What is a copper tube? Analysis of material composition and basic characteristics Definition of copper tube Copper tube is a tubular object made of co...
See Details -

Understanding Copper Square Tubes: Composition, Grades, and Typical Applications Copper square tubes are specialized extrusions that combine the super...
See Details

 English
English Español
Español 中文
中文